Technology Overview
Externally Stimulated
The Injectrode is deployed fully inside the body, and stimulated electrically through the skin, meaning there are no wires sticking out of the body after the simple placement procedure. No cables crossing the skin to connect to an outside simulator means less risk for infection or irritation.
Elegant Procedure
The simplicity of the procedure allows clinicians to help more patients with an outpatient procedure. After 15 minutes of training, 6 clinicians successfully placed the Injectrode in fewer than 5 minutes on their first attempt. After a bit of practice, the procedure was completed in under two minutes.*
*data on file

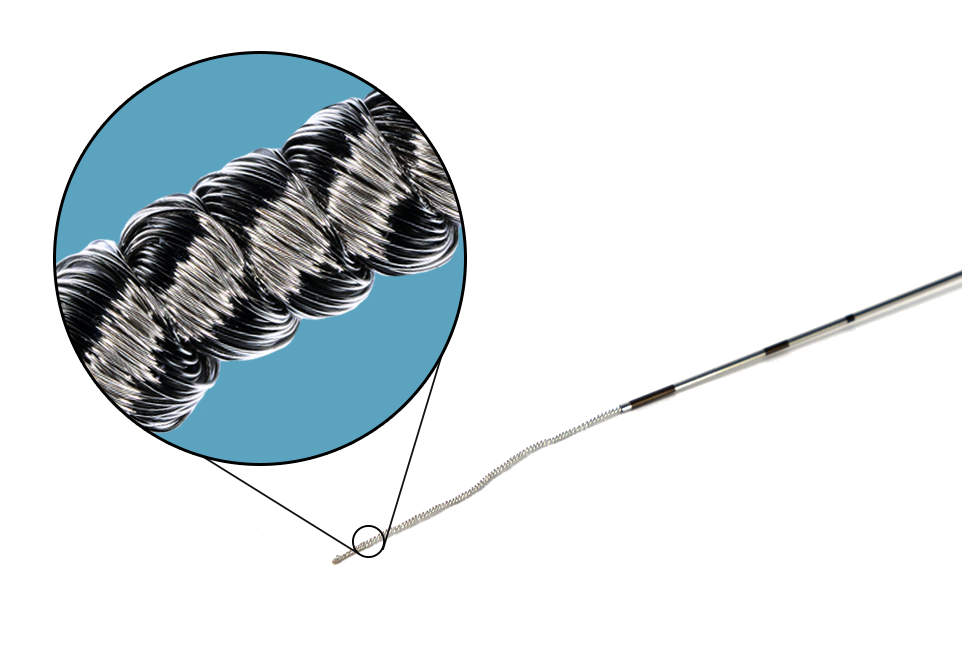
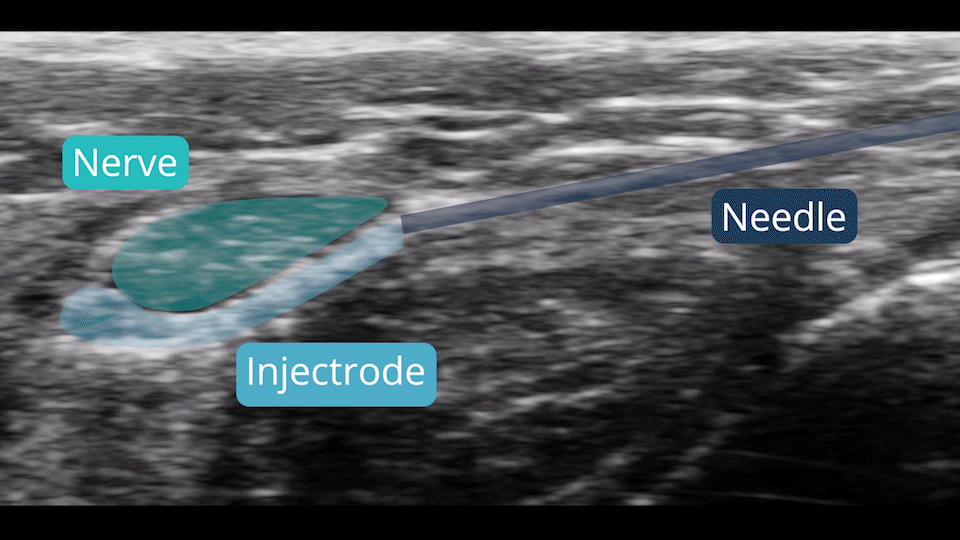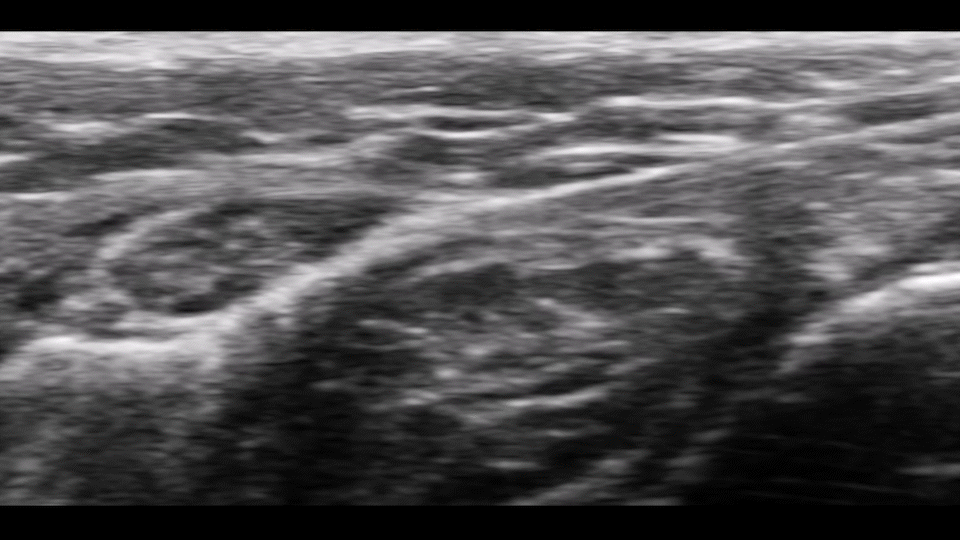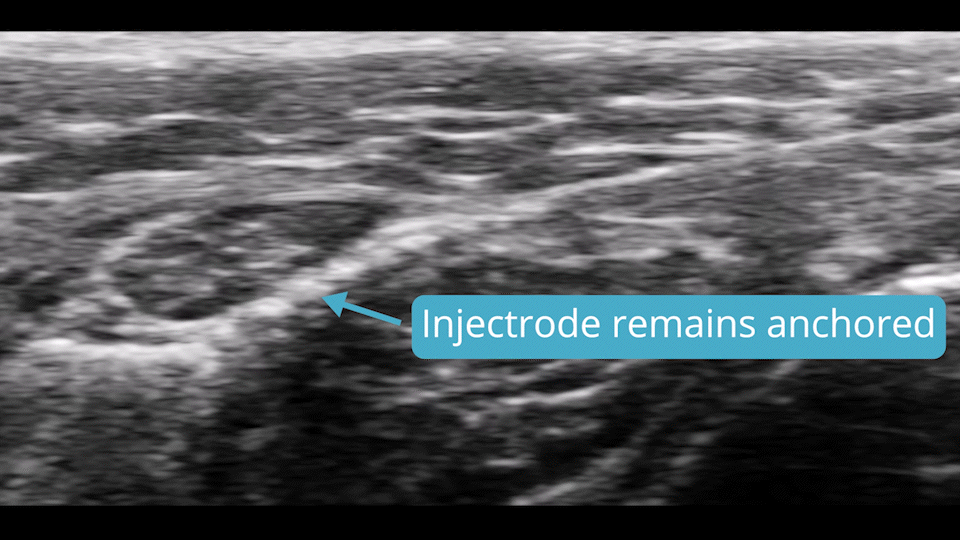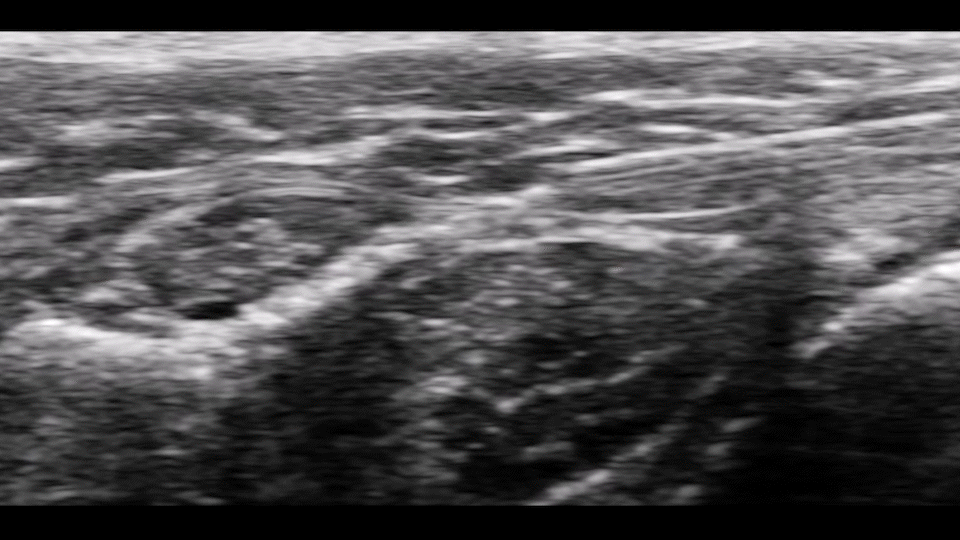
The Injectrode system enables access to difficult-to-reach nerves through a simple 18-ga needle injection, similar to a steroid injection, requiring no sutures for placement. Built with removal in mind, the helical wire structure allows each coil to lengthen and pull inwards sequentially when extracted, ensuring clean removal from the body while reducing scarring risk.
Simple to place.
Simple to remove.
How is it powered?
The Injectrode receives power from outside the body. The electrical power and waveforms come from an external pulse generator (EPG) that snaps magnetically onto a stimulating patch electrode. The patch is placed directly over the implanted Injectrode. When the EPG is powered on and stimulating, the Injectrode creates a conductive path for the electrical current to travel to the nerve target.
Resists Migration
Migration is one of the main pain points for clinicians when placing leads and electrodes. The Injectrode is designed to greatly minimize the risk of lead migration by self-anchoring and conforming to the patient's anatomy automatically, all without tines, hooks, or sutures. The anchoring capability is even achieved in curved injection pathways.
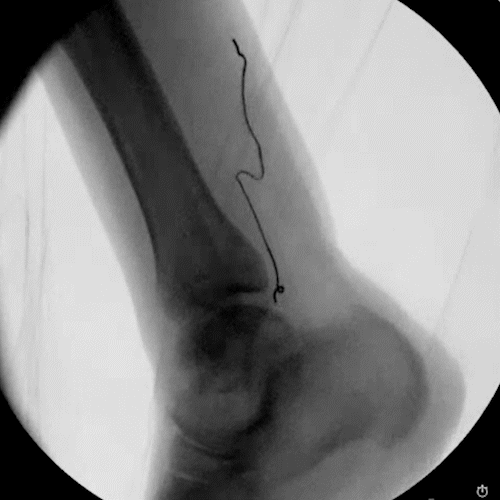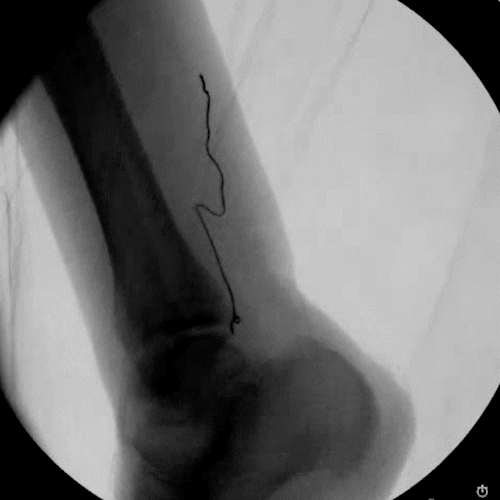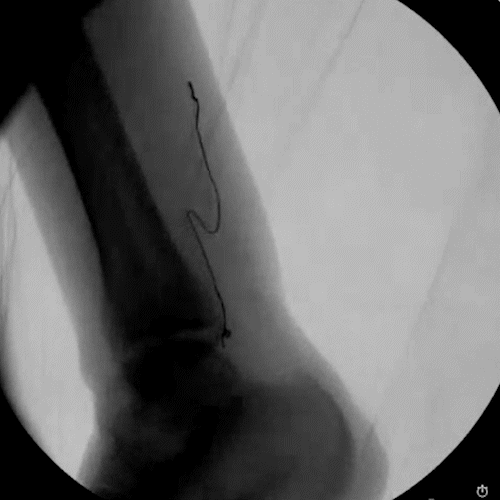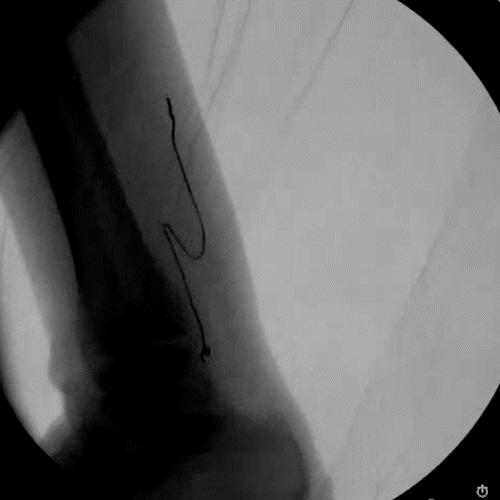
Ultrasound & Fluoroscopy Visualization
Placement is everything in neuromodulation, which is why device visualization is key. The Injectrode appears hyperechoic under ultrasound and displays a large acoustic shadow, allowing for clear imaging during placement. The device can also be readily imaged with fluoroscopy.